What is the most common type of gum disease?
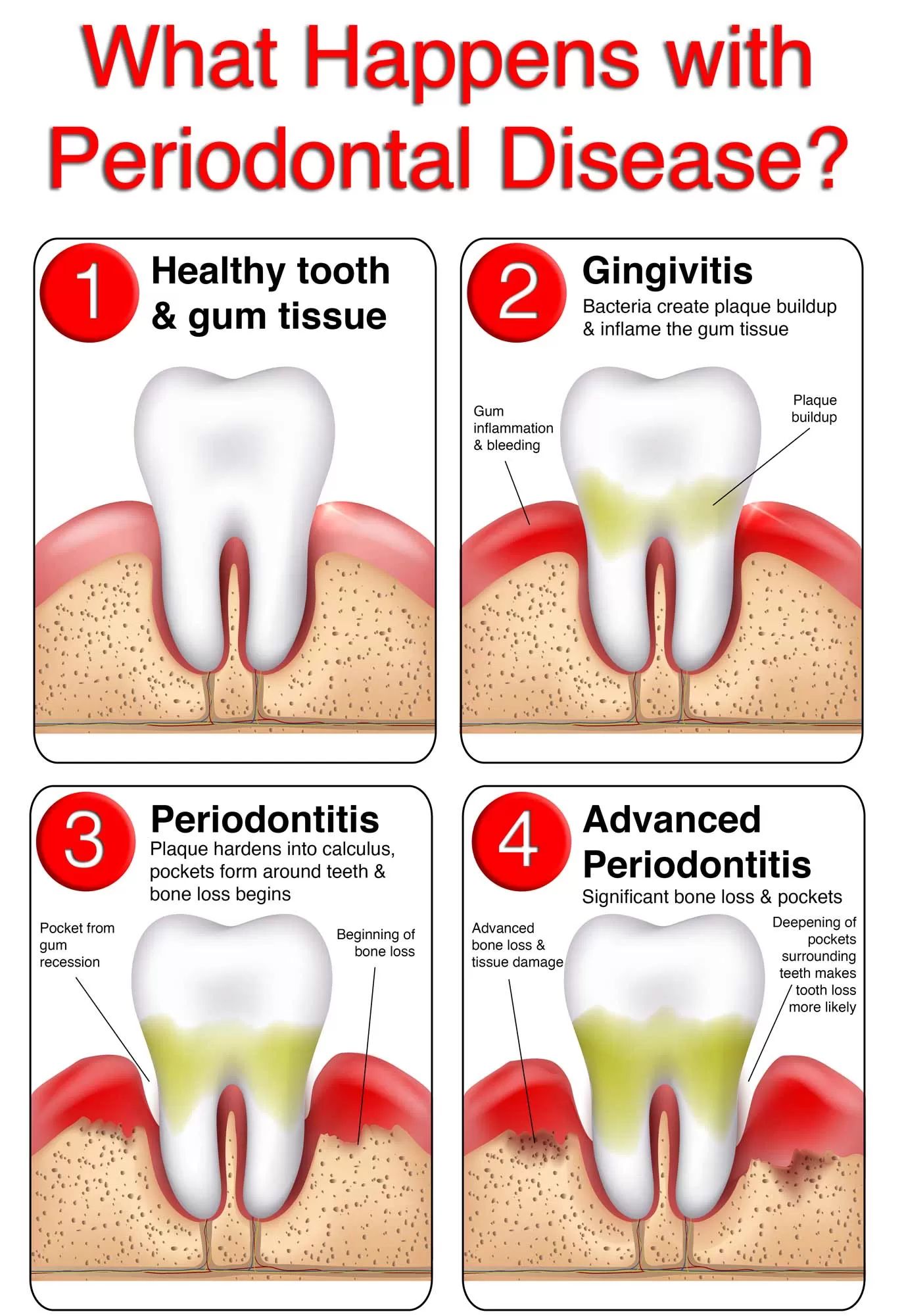
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a significant oral health issue that affects the tissues surrounding the teeth. It is primarily caused by the accumulation of plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—on the teeth and gums. There are two main types of gum disease: gingivitis and periodontitis, each with distinct characteristics and implications for oral health.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease and is characterized by inflammation of the gums. The primary cause of gingivitis is poor oral hygiene, which leads to plaque buildup on the teeth. Symptoms include red, swollen gums that may bleed during brushing or flossing. Although gingivitis is often mild and reversible with proper dental care, if left untreated, it can progress to more severe forms of gum disease.
Causes
The primary cause of gingivitis is plaque accumulation due to inadequate oral hygiene practices. Other contributing factors may include smoking, hormonal changes (such as those occurring during pregnancy or menstruation), certain medications that reduce saliva flow, and underlying health conditions like diabetes.
Symptoms
Common symptoms associated with gingivitis include:
- Swollen or puffy gums
- Redness in the gum tissue
- Bleeding while brushing or flossing
- Bad breath (halitosis)
Treatment
Treatment for gingivitis typically involves professional dental cleaning to remove plaque and tartar buildup. Patients are also advised to improve their oral hygiene practices at home by brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and flossing regularly.
Periodontitis
If gingivitis is not treated effectively, it can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease that can lead to tooth loss if not addressed promptly. Periodontitis involves deeper inflammation that affects not only the gums but also the bone supporting the teeth.
Stages
Periodontitis can be classified into several stages:
- Slight Periodontitis: Characterized by minor bone loss around teeth.
- Moderate Periodontitis: Involves increased bone loss and potential mobility in teeth.
- Severe Periodontitis: Significant bone loss occurs; teeth may become loose or shift position.
Causes
Similar to gingivitis, periodontitis is primarily caused by prolonged plaque buildup leading to chronic inflammation. Risk factors include genetic predisposition, smoking habits, poor nutrition, diabetes, and certain systemic diseases.
Symptoms
Symptoms of periodontitis may include:
- Persistent bad breath
- Receding gums (gums pulling away from teeth)
- Formation of pockets between teeth and gums
- Loose or shifting teeth
Treatment
Management of periodontitis often requires more intensive treatment than gingivitis. This may involve scaling and root planing (a deep cleaning procedure), antibiotics to control infection, and possibly surgical interventions in advanced cases.
Conclusion
Understanding the types of gum disease—gingivitis and periodontitis—is crucial for maintaining good oral health. Early detection through regular dental check-ups can prevent progression from gingivitis to periodontitis, thereby preserving both dental structure and overall health.
Types of Gum Disease
Explore the types of gum disease and learn about gingivitis and periodontitis for better oral health and hygiene.