Most Common Causes of Bleeding Gums
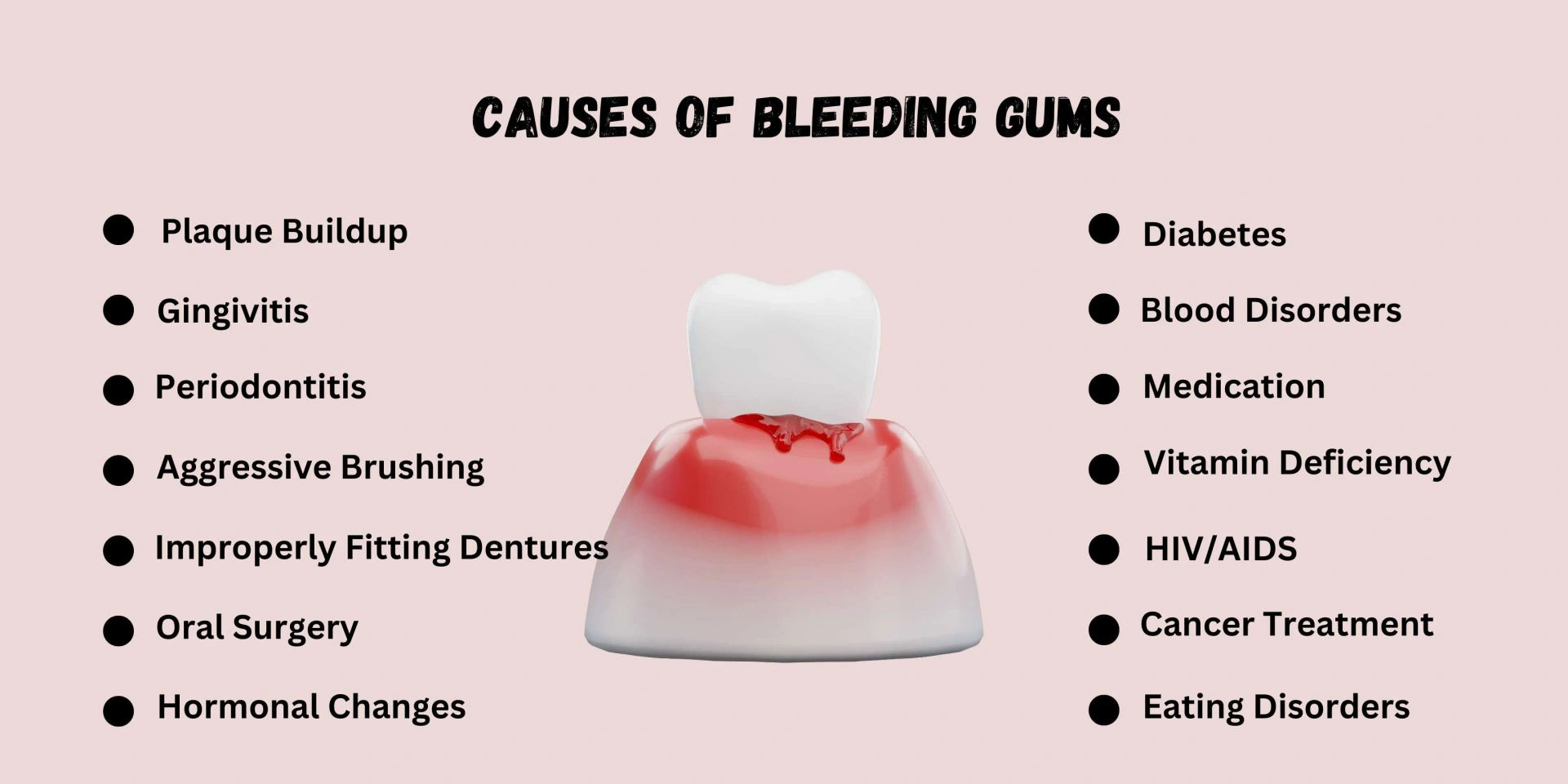
Bleeding gums, medically known as gingival bleeding, is a common condition that can indicate various underlying health issues. The primary causes of bleeding gums are often related to oral hygiene practices, systemic health conditions, and lifestyle factors.
Poor Oral Hygiene
One of the most prevalent causes of bleeding gums is inadequate oral hygiene. When plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—accumulates on the teeth and gums, it can lead to inflammation known as gingivitis. This condition is characterized by swollen, red gums that bleed easily during brushing or flossing. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease that can result in tooth loss and other serious complications (The Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy).
Nutritional Deficiencies
Nutritional deficiencies play a significant role in the health of the gums. Specifically, a lack of vitamin C can lead to scurvy, which manifests as swollen and bleeding gums. Vitamin C is essential for collagen synthesis and tissue repair; thus, its deficiency compromises gum integrity (Encyclopedia of Human Nutrition). Other deficiencies, such as vitamin K and folic acid, may also contribute to gum bleeding due to their roles in blood clotting and cellular function.
Systemic Health Conditions
Certain systemic health conditions can manifest symptoms in the oral cavity, including bleeding gums. Conditions such as diabetes mellitus can impair blood flow and immune response, making individuals more susceptible to infections like periodontal disease (Journal of Periodontology). Additionally, blood disorders such as thrombocytopenia or hemophilia affect the body’s ability to clot properly, leading to increased bleeding from the gums.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause can also cause changes in gum tissue sensitivity and increase susceptibility to gingival inflammation (American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology). For instance, pregnant women may experience pregnancy gingivitis due to elevated hormone levels that enhance blood flow to the gums.
Tobacco Use
Tobacco use is another significant risk factor for gum disease and subsequent bleeding. Smoking impairs blood circulation in the gums and reduces healing capacity while promoting bacterial growth within the oral cavity (Oral Diseases). Smokers are at a higher risk for developing periodontal diseases compared to non-smokers.
Medications
Certain medications may have side effects that contribute to gum bleeding. Anticoagulants (blood thinners) like warfarin or aspirin increase bleeding tendencies throughout the body. Additionally, some antihypertensive medications may cause gingival hyperplasia—a condition where gum tissue overgrows—leading to increased chances of bleeding (Dental Clinics of North America).
Conclusion
In summary, bleeding gums can arise from various factors including poor oral hygiene practices leading to gingivitis or periodontitis; nutritional deficiencies particularly involving vitamins C and K; systemic health conditions like diabetes; hormonal changes; tobacco use; and certain medications. Addressing these underlying causes through improved dental care routines and medical consultation is crucial for maintaining optimal gum health.
Most Common Causes of Bleeding Gums
Find out the causes of bleeding gums and why maintaining oral hygiene is crucial for preventing gum disease and complications